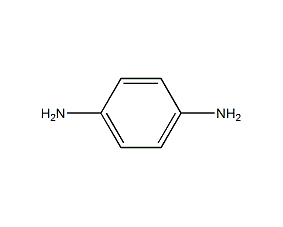
Structural formula
| Business number | 02TN |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H8N2 |
| Molecular weight | 108.14 |
| label |
C.I. oxidation chromogenic base 10, p-diaminobenzene, Fur black D, fur dollar D, Urs D, Ursi black D, Urz D, p-phenylenediamine, 1,4-Benzendiamine, 1,4-Di-aminobenzol, 4-Phenylendiamine, Aminogen II, Aromatic nitrogen-containing compounds and their derivatives, Pyroelectric crystal materials |
Numbering system
CAS number:106-50-3
MDL number:MFCD00007901
EINECS number:203-404-7
RTECS number:SS8050000
BRN number:742029
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1.Characteristics: white to lavender crystal. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): 145~147[2]
3. Boiling point (℃) : 267[3]
4. Relative vapor density (air=1): 3.7[4]
5. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 0.14 (100℃) [5]
6. Critical pressure (MPa): 5.18[6]
7. Octanol/water partition coefficient: -0.25~-0.7[7]
8. Flash point (℃): 155[8 ]
9. Explosion upper limit (%): 9.8[9]
10. Explosion lower limit (%): 1.3 [10]
11. Solubility: Slightly soluble in water, soluble in ethanol, ether, benzene, chloroform and acetone. [11]
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[12] LD50: 80mg/kg (rat oral)
2. Irritation[13] Human transdermal: 250mg (24h), mild irritation.
3. Mutagenicity [14] Microbial mutagenicity: Salmonella typhimurium 2μmol/dish. DNA inhibition: 200 mg/kg orally for mice. Cytogenetic analysis: Hamster ovary 15mg/L. Sex chromosome deletion and non-disjunction: Drosophila melanogaster orally administered 15500 μmol/L (3d).
4. Carcinogenicity [15] IARC Carcinogenicity Comment: G3, insufficient evidence of carcinogenicity to humans and animals.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[16]
LC50: 5.74mg/L (48h) (goldfish)
EC50: 74mg/L (60h) (Tetrahymena pyriformis); 37mg/L (30min) (Photoluminous bacteria, Microtox toxicity test)
2. Biodegradability[17 ]
Aerobic biodegradation (h): 168~672
Anaerobic biodegradation (h): 672~2688
3. Non-biodegradability[18]
Photolysis Maximum Light Absorption – High (nm): 308
Water Photooxidation half-life (h): 30~1740
Photooxidation half-life in air (h): 0.28~2.8
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 34.72
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 93.9
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 258.9
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 57.5
5. Dielectric constant:
6. Dipole moment (10-24cm3):
7. Polarizability: 13.76
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 2
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 52
7. Number of heavy atoms: 8
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 54.9
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Toxic. Its toxicity is basically the same as o-phenylenediamine. Oral lethal dose for rabbits is 250mg/kg. See o-phenylenediamine for details.
2. Poisoning can be caused by absorption through the skin or inhalation of dust. Poisoning is mostly caused by absorption through the skin. Reactions to the skin vary, with acute, severe eruptive eczema reaching the back, face, and abdomen, with erysipelas-like crusts. The effects of its dust on the respiratory tract are also different, and can cause symptoms such as rhinitis, bronchitis, frequent fever, unique wheezing, and vagus nerve tension due to tracheal inflammation. For rabbits, the lowest oral lethal dose is 300mg/kg. The maximum allowable concentration of paraphenylenediamine in the workplace is 0.1mg/m3.
3. Stability[19] Stable
4. Incompatible substances[20] Strong oxidants, acids, acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, chloroform
5. Conditions to avoid contact[21] Heating
6. Polymerization hazard[22] No polymerization
Storage method
1. Storage precautions[23] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The packaging is sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, acids, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. Suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills.
2. Use airtight packaging in iron drums. Store in a cool, ventilated and dry place. Heat, moisture and sun protection. Store and transport toxic and flammable chemicals according to regulations.
Synthesis method
1. Obtained from the reduction of p-nitroaniline with iron powder in acidic medium. Put the iron powder into hydrochloric acid, heat it to 90°C, and add p-nitroaniline while stirring. After the addition is completed, react at 95-100°C for 0.5h, and then add concentrated hydrochloric acid dropwise to complete the reduction reaction. After cooling, neutralize with saturated sodium carbonate solution to pH 7-8, boil and filter while hot, and wash the filter cake with hot water. Combine the filtrate and washing liquid, concentrate under reduced pressure, crystallize by cooling or distill under reduced pressure to obtain p-phenylenediamine with a yield of 95%.
![]()
2. Dichlorophenylamine Solution Preparation process 1: Add 170g of copper chloride dihydrate (0.01mol) to the autoclave with a stirrer, then cool, add 15g of 28% ammonia water with stirring, and then add 0.74g of p-dichlorobenzene (0.005mol) ). React at 210°C for 6 hours. Add 50 ml of tetrahydrofuran to the reaction mixture, filter the solid material, and wash it thoroughly with 30 ml of tetrahydrofuran. The filtrate and washing liquid are combined, and the p-phenylenediamine content is 90%. Preparation process 2: Add 92.0 parts of p-dichlorobenzene, 127.7 parts of ammonia, 127.7 parts of water (parts by mass) and 2.0 parts of copper chloride into an autoclave with a stirrer, and react at 200°C for 5 hours under the stirrer. After the reaction is completed, the autoclave is cooled to 90°C and ammonia is released. 105.4 parts of sodium hydroxide aqueous solution was added to the reaction product to neutralize the free amine. The conversion rate of p-dichlorobenzene is 99.7%, and the selectivity of p-phenylenediamine is 92.4%.
Purpose
1. As a dye intermediate, epoxy resin curing agent, and rubber antioxidant DNP, DOP, DBP, etc. production.
2. This product is mainly used to manufacture azo dyes and sulfur dyes, etc. It can also be used for fur dyeing (such as fur black D, fur blue black DB, fur brown N2, etc.), and can also be used as cosmetic hair dye. It is the main dye for dyeing black hair and can be used in the production of rubber antioxidants DNP, DOP, DBP and imaging agents.
3. As a dye intermediate, epoxy resin curing agent, and used in the production of rubber antioxidants DNP, DOP, DBP, etc. [24]

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

