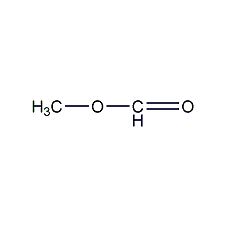
Structural formula
| Business number | 02V3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C2H4O2 |
| Molecular weight | 60.05 |
| label |
Methyl formate, Formic acid methyl ester, Methyl methanoate, Formic ether |
Numbering system
CAS number:107-31-3
MDL number:MFCD00003291
EINECS number:203-481-7
RTECS number:LQ8925000
BRN number:1734623
PubChem number:24857508
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless liquid with aromatic odor. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -99.8[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 31.5[3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 0.98[4]
5. Relative vapor Density (air=1): 2.07[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 64 (20℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -973[7]
8. Critical temperature (℃): 214[8]
9. Critical pressure (MPa): 6.00[9]
10. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 0.03 [10]
11. Flash point (℃): -19 (CC) [11]
12. Ignition temperature ( ℃): 449[12]
13. Explosion upper limit (%): 20[13]
14. Explosion Lower limit (%): 5.9[14]
15. Solubility: soluble in water, ethanol, ether, and methanol. [15]
16. Viscosity (mPa·s, 25ºC): 0.328
17. Flash point (ºC, closed): -26
18. Flash point (ºC, open): -32
19. Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol, 31.5ºC): 28.26
20. Heat of fusion ( KJ/mol): 7.45
21. Heat of formation (KJ/mol): 378.47
22. Specific heat capacity (KJ/(kg·K), 15~20ºC, constant pressure) : 2.00
23. Boiling point rising constant (25ºC): 1.649
24. Conductivity (S/m, 20ºC): 3.6×10-5
25. Relative density (20℃, 4℃): 0.9742
26. Relative density (25℃, 4℃): 0.9664
27. Normal temperature Refractive index (n25): 1.3415
28. Critical density (g·cm-3): 0.349
29 .Critical volume (cm3·mol-1): 172
30. Critical compression factor: 0.255
31. Eccentricity factor: 0.254
32. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5: 20.503
33.van van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1): 5.090×109
34. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol-1): 32.510
35. Liquid phase standard heat of combustion (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1 ): -972.61
36. Liquid phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -386.10
37 .Gas phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -1003.20
38. Gas phase standard claimed heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1 ): -355.51
39. Gas phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 284.14
40. Gas phase standard formation free energy (kJ·mol-1): -297.82
41. Gas phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1 ·K-1): 66.53
Toxicological data
1. AcuteProperties: Rabbit oral LD50: 1622mg/kg;
2. Its vapor has anesthetic effect. Irritates the nasal mucosa, causes vomiting, drowsiness, and corrodes the lungs. Inhalation can act on the central nervous system and cause visual and other disorders. The maximum allowable concentration is 245.4mg/m3 (0.25mg/L air). There is a fatal risk if exposed to 1% methyl formate vapor for 2.5 hours or 5% methyl formate vapor for 30 minutes. Guinea pigs will die after being exposed to methyl formate 128g/mL for 30 minutes.
3. Acute toxicity[16]
LD50: 475mg/kg (rat Oral); 1622mg/kg (rabbit oral)
LC50: 5200mg/m3 (rat inhalation, 4h)
4 . Irritation No information available
5. Subacute and chronic toxicity[17] Cat inhalation 2300mg/m3, 25h, movement disorder after 1.5h, death within 2~3h of lying on side (pulmonary edema).
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[18]
LC50: 120mg/L (96h) (Yuanweiya Luoyu, static)
EC50: >500mg/L (24h) (Daphnia); 190mg/L (96h) (Scenedesmus)
2. Biodegradation PropertiesNo information available
3. Non-biodegradability[19] In the air, when hydroxyl When the free radical concentration is 5.00×105/cm3, the degradation half-life is 71d (theoretical).
When the pH value is 7 and 8, the hydrolysis half-life is 5.1d and 12d respectively (theoretical).
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 13.24
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 65.2
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 140.2
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 21.3
5. Polarizability: 5.25
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 26.3
7. Number of heavy atoms: 4
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 18
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Stability[20] Stable
2. Incompatible substances[21] Strong oxidants, alkalis
3. Polymerization hazard[22] No polymerization
Storage method
Storage Precautions[23] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 29°C. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants and alkalis, and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
1. Direct esterification method: obtained by esterification of formic acid and methanol. Mix anhydrous calcium chloride and formic acid, stir and cool. Add methanol slowly. Reflux for 2.5h and distill to obtain the finished product. During the reaction, formic acid and methanol can also be heated to reflux without adding calcium chloride, and the distillate with a relative density of 0.947 can be collected by distillation to obtain methyl formate with a yield of 90%. Raw material consumption quota: formic acid 845kg/t, methanol 600kg/t.
![]()
2. Carbon dioxide method in trifluoride In the methanol solution of boron, an iridium complex is used as a catalyst, carbon dioxide and hydrogen are introduced, and the reaction proceeds at 100°C and 5.88MPa to generate methyl formate.
3. Methanol carbonylation method.
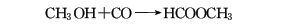
4. Methanol dehydrogenation method.
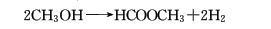
5. Methanol oxidative dehydrogenation method .
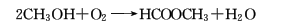
6. One-step synthesis of synthesis gas .
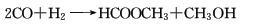
Refining method: easily contained impurities are free formic acid and methanol. When refining, add anhydrous potassium carbonate to dry and then distill, or add phosphorus pentoxide and fractionate on a water bath at 80~90°C. You can also wash with concentrated sodium carbonate aqueous solution first, dry with solid sodium carbonate, and then add phosphorus pentoxide for fractionation.
7.After mixing anhydrous calcium chloride and formic acid, cool and stir, slowly add methanol, and reflux for 25 hours to react:

Then distill to obtain the crude product, which is dried with anhydrous sodium carbonate to remove acid and filtered to obtain the finished product.
Purpose
1. Used as raw material for organic synthesis, it can produce formic acid, formamide, dimethylformamide, ethylene glycol, trichloromethyl chloroformate, oxalate, acetic anhydride, acetic acid, etc.
2. Used in the production of pesticides, military gases and solvents; used as nitrocellulose, cellulose acetate solvents, fumigation pesticides and fungicides.
3. Formylating agent in organic synthesis. Others can also be used for spices, drying fruits, processing cereals, etc.
4. Used as a fungicide, fumigant, and tobacco treatment. It is also a raw material for organic synthesis, such as hydrolysis of MeF to produce formic acid; amination to produce formamide and dimethylformamide; coupling of carbon-based compounds to produce ethylene glycol, synthesis of trichloromethyl chloroformate (diphosgene), and ethanol. Diacid ester can be dehydrated to produce acetic anhydride, and isomerized to produce acetic acid, etc.
5. Used in organic synthesis as a solvent, pesticide, bactericide and analytical reagent for cellulose acetate. [24]
1. Used as raw material for organic synthesis, it can produce formic acid, formamide, dimethylformamide, ethylene glycol, trichloromethyl chloroformate, oxalate, acetic anhydride, acetic acid, etc.
2. Used in the production of pesticides, military gases and solvents; used as nitrocellulose, cellulose acetate solvents, fumigation pesticides and fungicides.
3. Formylating agent in organic synthesis. Others can also be used for spices, drying fruits, processing cereals, etc.
4. Used as a fungicide, fumigant, and tobacco treatment. It is also a raw material for organic synthesis, such as hydrolysis of MeF to produce formic acid; amination to produce formamide and dimethylformamide; coupling of carbon-based compounds to produce ethylene glycol, synthesis of trichloromethyl chloroformate (diphosgene), and ethanol. Diacid ester can be dehydrated to produce acetic anhydride, and isomerized to produce acetic acid, etc.
5. Used in organic synthesis as a solvent, pesticide, bactericide and analytical reagent for cellulose acetate. [24]

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

