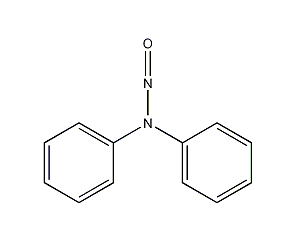
Structural formula
| Business number | 01WK |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C12H10N2O |
| Molecular weight | 198.22 |
| label |
diphenylnitrosamine, N-nitroso-N-phenylaniline, Highly efficient polymerization inhibitor N-NO, Anti-scorch agent NA, Diphenyl nitrosamine, N-nitroso-N-phenyl aniline, Polymerization inhibitor |
Numbering system
CAS number:86-30-6
MDL number:MFCD00019920
EINECS number:201-663-0
RTECS number:JJ9800000
BRN number:909531
PubChem number:24886620
Physical property data
1. Properties: yellow to brown powder or flake crystal
2. Density (g/cm3): 1.24
3. Relative Vapor density (g/mL, air=1): Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC): 66.5
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 268
6. Boiling point (ºC, 5.2kPa): Undetermined
7. Refractive index: Undetermined
8. Flash point (ºC): Undetermined
9. Specific rotation (º): Undetermined
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Undetermined
11. Vapor pressure (kPa, 25ºC): Undetermined
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, 60ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
18. Explosion lower limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Insoluble in water (0.0035 g/100 mL). Easily soluble in organic solvents such as acetone, hot benzene, hot ethanol, ethyl acetate, methylene chloride, carbon tetrachloride, carbon disulfide, N, N-dimethylformamide and ether.
Toxicological data
1. Toxicity classification Poisoning 2. Acute toxicity Oral administration – rat LD50: 1825 mg/kg; Oral administration – mouse LD50: 1860 mg/kg. 3. Irritation data Eyes – Rabbit 500 mg/24 hours Mild.
4. It is irritating to the skin, glasses and upper respiratory tract. Long-term exposure will cause changes in liver function and blood, and cause symptoms such as neurasthenia. During the production process, attention should be paid to the tightness of the equipment and the ventilation of the workshop, and operators should wear protective equipment. Eating and drinking in the production premises is not allowed.
Ecological data
This product slightly pollutes water bodies.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 60.61
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 181.5
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K): 467.6
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 44.0
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 24.02
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 3
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 2
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 32.7
7. Number of heavy atoms: 15
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 178
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
Rearrangement reaction can occur in methanol hydrochloric acid solution to form p-nitrosodiphenylamine. This product is easily oxidized. It is an organic drug.
Storage method
Stored in a cool, ventilated warehouse, fireproof, sunproof and airtight.
Synthesis method
1. Obtained from the reaction of diphenylamine and sodium nitrite in the presence of sulfuric acid: the nitrosation reaction uses ethanol or xylene (or chlorobenzene) as the solvent, the sodium nitrite solution content is 40%, and the concentrated sulfuric acid content is 30% , react at about 26℃ for 2.5-3h. The reaction product is washed with water until the pH value is 6-7. When ethanol is used as the solvent, a solid product is obtained after drying; when xylene or chlorobenzene is used as the solvent, a liquid product is obtained, and the product needs to be dried with calcium chloride.
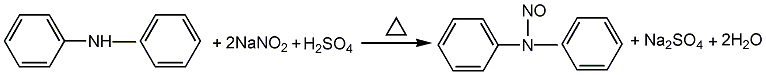
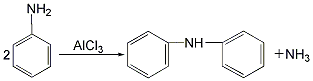
2. Anhydrous aniline Aluminum chloride is used as a catalyst to carry out the condensation reaction. The reaction product is precipitated with hydrochloric acid, neutralized with sodium hydroxide, boiled, washed, vacuum distilled, crystallized with ethanol, and separated to obtain the finished product.
Purpose
1. In the rubber processing industry, it is used as an anti-scorch agent, vulcanization retardant (vulcanization retardant), and college polymerization inhibitor of chloroprene rubber; it is also used as an insecticide and disinfectant; it is also used as an anti-aging agent. Agent 4010 and intermediates of dyes.
2. Used as natural rubber, synthetic Anti-scorch agent for rubber (except butyl rubber), which can increase the safety of rubber mixing operations; it can also be used as a re-plasticizer for slightly scorched rubber. It is particularly effective for compounds containing alkaline accelerators such as thiazoles, thiurams and dithiocarbamates, especially for rubber containing thiazole-guanidine and thiazole-thiuram accelerator systems; it is particularly effective for compounds containing aldehydes and amines The accelerator has little effect on the rubber and is not suitable for thiuram sulfur-free vulcanized rubber. It can replace wood tar as an efficient polymerization inhibitor for chloroprene rubber. It is also an important raw material for antioxidant 4010 and dye intermediate RT color base.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

